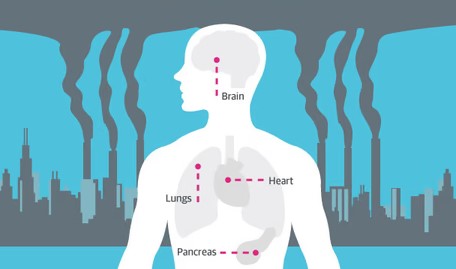
In today’s modern world, air pollution is a growing concern that affects millions of people worldwide. The air pollution health effects are not limited to just the environment but extend deeply into our physical and mental well-being. Pollutants such as particulate matter, ground-level ozone, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide infiltrate the air we breathe, contributing to a host of health issues. As urbanization increases and industrial activities continue, exposure to polluted air has become unavoidable for many, making it essential to understand the impact of air quality on overall health. This article will explore the various ways in which air pollution affects human health and how clean air can significantly improve wellness.
Understanding Air Pollution and Its Sources
Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the atmosphere that can have a detrimental impact on human health and the environment. These pollutants come from a variety of sources, both natural and human-made. Natural sources of pollution include wildfires, volcanic eruptions, and dust storms. However, the primary contributors to poor air quality are human activities, such as vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and the burning of fossil fuels.
Major Pollutants and Their Impact
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): These tiny particles, often invisible to the naked eye, are released into the air from sources like vehicle exhaust, construction sites, and power plants. PM2.5 (particles less than 2.5 micrometers in diameter) and PM10 (particles less than 10 micrometers in diameter) are particularly harmful because they can enter the respiratory system, affecting the lungs and even reaching the bloodstream. Long-term exposure to particulate matter is linked to respiratory diseases such as asthma, bronchitis, and lung cancer.
- Ground-Level Ozone (O₃): Ozone at ground level is a result of chemical reactions between pollutants emitted by vehicles and industrial facilities in the presence of sunlight. It can irritate the lungs, causing conditions like asthma, coughing, and shortness of breath. Long-term exposure may also worsen chronic respiratory diseases.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Nitrogen oxides are primarily emitted from vehicle exhaust and power plants. They contribute to the formation of both ground-level ozone and particulate matter, and long-term exposure to nitrogen oxides has been shown to aggravate respiratory conditions and impair lung function.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂): This pollutant is released by power plants, industrial processes, and the burning of fossil fuels. It irritates the respiratory system, leading to asthma and other lung diseases, particularly in children and the elderly.
These pollutants have far-reaching effects on human health, often triggering both short-term and long-term illnesses, and exacerbating existing health conditions. As the air quality deteriorates, it becomes vital for individuals to understand the potential health risks associated with prolonged exposure to these pollutants.
Air Pollution Health Effects: Impact on Respiratory and Cardiovascular Health
1. Respiratory Health Risks
The respiratory system is perhaps the most affected by poor air quality. Pollutants like particulate matter, ground-level ozone, and nitrogen oxides can significantly impair lung function. Short-term exposure to high levels of air pollution may cause coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and irritation in the eyes and throat. In vulnerable groups, such as children and the elderly, these effects are more pronounced and may lead to exacerbated conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Long-term exposure to air pollution is even more concerning. Research shows that individuals living in areas with consistently high pollution levels are at a greater risk of developing chronic respiratory diseases, including emphysema and lung fibrosis. Additionally, air pollution has been associated with a higher incidence of lung cancer. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), air pollution is one of the leading causes of preventable deaths globally, primarily due to respiratory diseases and complications related to air quality.
2. Cardiovascular Health Risks
In addition to its impact on the lungs, air pollution also significantly affects the cardiovascular system. Studies have shown that long-term exposure to pollutants can lead to heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems. Particulate matter, in particular, has been linked to the development of atherosclerosis (the buildup of plaque in the arteries), which restricts blood flow and increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
The mechanism behind this involves the inflammatory response triggered by inhaling polluted air. Particulate matter and other pollutants cause systemic inflammation, which in turn can lead to the narrowing of blood vessels and increased blood pressure. For individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, the risks are even more severe.
The Connection Between Clean Air and Mental Health
While the physical health impacts of air pollution are widely recognized, the psychological effects are often overlooked. Research has revealed a significant link between poor air quality and mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. Pollutants such as particulate matter and nitrogen oxides have been shown to affect the brain, particularly in children and older adults.
Exposure to air pollution can lead to oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, which is associated with a variety of mental health conditions. For example, studies have found that children living in areas with high levels of pollution may experience developmental delays, reduced cognitive function, and an increased risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Additionally, air pollution is known to affect sleep quality, leading to sleep disturbances and fatigue. Poor sleep, in turn, has been linked to mood disorders, decreased cognitive function, and reduced overall well-being. As mental health issues continue to rise globally, addressing air quality is an important step in improving public health.
Benefits of Clean Air for Overall Wellness
While air pollution health effects can be severe, the good news is that improving air quality can have immediate and long-lasting benefits for health and well-being. Clean air supports optimal lung function, reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease, and can even enhance mental clarity and emotional resilience.
- Improved Respiratory Health: When air quality improves, the risk of asthma attacks, bronchitis, and other respiratory issues is significantly reduced. Those with pre-existing conditions like COPD may experience fewer flare-ups and improved overall lung function.
- Cardiovascular Protection: Cleaner air means less exposure to harmful pollutants, which lowers the risk of heart disease and stroke. Individuals living in areas with better air quality tend to have lower rates of hypertension, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular problems.
- Enhanced Mental Health: Clean air has been linked to better mood, reduced anxiety, and improved cognitive function. By lowering exposure to environmental stressors, individuals experience a greater sense of well-being, better sleep quality, and a more balanced emotional state.
- Longevity: Ultimately, reducing exposure to air pollution can increase life expectancy. Cleaner environments lead to lower mortality rates, particularly from respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
In conclusion, understanding the air pollution health effects is crucial for recognizing the importance of clean air in maintaining health and wellness. From the lungs and heart to the brain, air pollution has far-reaching consequences for physical and mental health. By improving air quality, we can significantly reduce the risk of chronic diseases, enhance cognitive function, and improve overall life satisfaction. Governments, industries, and individuals must work together to promote cleaner air, as the health benefits of cleaner air are undeniable. It’s time to prioritize air quality for the sake of our health and future well-being.