Chronic inflammation is often the underlying cause of many health conditions, including heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, and even cancer. An Anti-Inflammatory Diet is designed to help reduce the levels of inflammation in the body, potentially lowering the risk of these diseases and improving overall health. By incorporating the right foods into your daily meals and avoiding certain inflammatory foods, you can take proactive steps to support your body’s natural healing process. In this article, we’ll explore the key foods to include in an anti-inflammatory diet, as well as those you should avoid, for better long-term health.
What Is Inflammation and Why Does It Matter?
Inflammation is a natural immune response to injury, infection, or harmful stimuli. In the short term, inflammation is essential for the body’s healing process, as it helps fight infections, repair tissues, and protect against further damage. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can have detrimental effects on the body. Chronic inflammation has been linked to a variety of conditions, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Chronic inflammation can damage blood vessels, increase plaque buildup, and raise the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Arthritis: Inflammatory joint diseases like rheumatoid arthritis are directly related to prolonged inflammation.
- Metabolic Disorders: Conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and insulin resistance are linked to chronic low-grade inflammation.
- Neurological Disorders: Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive impairments have been associated with inflammatory processes in the brain.
An Anti-Inflammatory Diet helps reduce this long-term inflammation by focusing on foods that have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties, while steering clear of those that can exacerbate the issue.
Foods to Include in an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
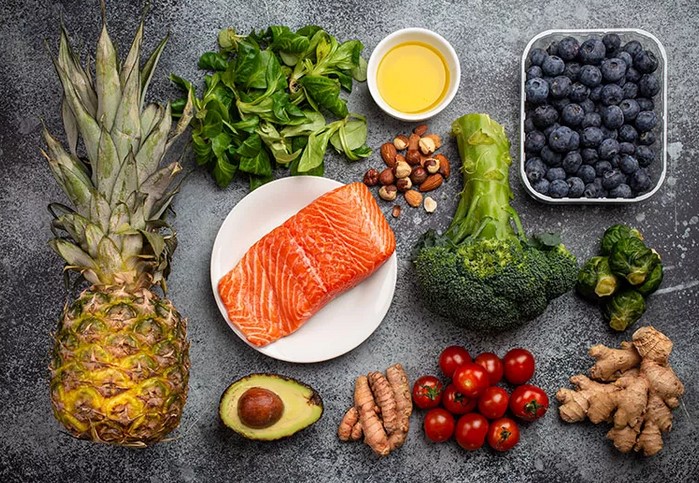
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet doesn’t require drastic changes; rather, it’s about choosing nutrient-dense foods that promote a healthy balance in the body. Here are some of the most powerful anti-inflammatory foods you should consider adding to your daily meals.
1. Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are the cornerstone of any anti-inflammatory diet. These foods are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that help combat oxidative stress and lower inflammation levels.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are packed with antioxidants called flavonoids, which have strong anti-inflammatory properties. These fruits can also help protect against oxidative stress that contributes to chronic disease.
- Leafy Greens: Kale, spinach, and Swiss chard are high in vitamin K, which helps reduce inflammation in the body. These vegetables are also packed with fiber and other anti-inflammatory compounds.
- Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts contain sulforaphane, a compound that can help reduce inflammation and protect against certain types of cancer.
2. Healthy Fats
Not all fats are created equal. While trans fats and saturated fats can promote inflammation, healthy fats, especially those rich in omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce it.
- Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil is a key component of the Mediterranean diet, known for its ability to reduce inflammation and improve heart health. It’s high in monounsaturated fats, which have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to reduce markers of inflammation in the body.
- Nuts and Seeds: Walnuts, almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are high in omega-3s and also contain antioxidants that help combat inflammation.
3. Herbs and Spices
Certain herbs and spices are incredibly potent anti-inflammatory agents. They not only add flavor to your meals but also offer a wide range of health benefits.
- Turmeric: This golden-yellow spice contains curcumin, a compound that has powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Curcumin has been shown to reduce inflammation in conditions like arthritis and may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Ginger: Ginger contains bioactive compounds such as gingerols, which are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Regular consumption of ginger can help reduce muscle soreness, improve digestion, and ease joint pain.
- Garlic: Garlic has long been associated with immune-boosting and anti-inflammatory effects. Allicin, the active compound in garlic, has been shown to reduce markers of inflammation and support heart health.
4. Whole Grains
Refined grains, such as white bread and pasta, can increase inflammation in the body, but whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats have the opposite effect. They are high in fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and lower inflammation.
- Oats: Rich in beta-glucans, a type of soluble fiber, oats help regulate cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation, particularly in the digestive system.
- Quinoa: A gluten-free grain that provides plant-based protein, fiber, and antioxidants, quinoa helps reduce inflammation and support overall health.
Foods to Avoid in an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
While it’s important to focus on foods that fight inflammation, it’s equally important to avoid foods that trigger or worsen chronic inflammation. These foods can promote oxidative stress, disrupt the balance of hormones, and contribute to disease progression.
1. Processed Foods and Sugars
Highly processed foods, including sugary snacks, sodas, and packaged baked goods, are some of the leading culprits behind chronic inflammation. These foods are often high in refined sugars and unhealthy fats, both of which can contribute to inflammatory responses in the body.
- Refined Sugar: Excessive sugar intake has been shown to elevate blood sugar levels and increase the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which exacerbate chronic inflammation.
- Processed Snacks: Many processed foods contain trans fats, which are highly inflammatory and can increase the risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions.
2. Refined Carbohydrates
Refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, pastries, and certain breakfast cereals, have a high glycemic index, meaning they cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. This can trigger an inflammatory response in the body, leading to insulin resistance and chronic disease.
3. Fried Foods
Fried foods, including French fries and fried chicken, are often cooked in unhealthy oils that contain high levels of omega-6 fatty acids. While omega-6s are essential for health, an excess of these fats in the diet, particularly when not balanced with omega-3s, can promote inflammation and increase the risk of diseases such as heart disease and obesity.
4. Red Meat and Processed Meats
While lean cuts of meat can be part of a healthy diet, excessive consumption of red meat, particularly processed meats like sausages, bacon, and hot dogs, has been linked to inflammation. These meats are high in saturated fats and advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which can contribute to inflammatory processes in the body.
Adopting an Anti-Inflammatory Diet is a proactive and effective way to reduce chronic inflammation and support long-term health. By prioritizing anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, healthy fats, whole grains, and spices, while avoiding inflammatory foods such as processed sugars, refined carbs, and unhealthy fats, you can help manage inflammation and lower the risk of many chronic diseases. Incorporating these foods into your daily routine will not only improve your overall well-being but may also contribute to a longer, healthier life. It’s never too late to start; small changes in your diet can make a significant difference in managing inflammation and boosting your health.